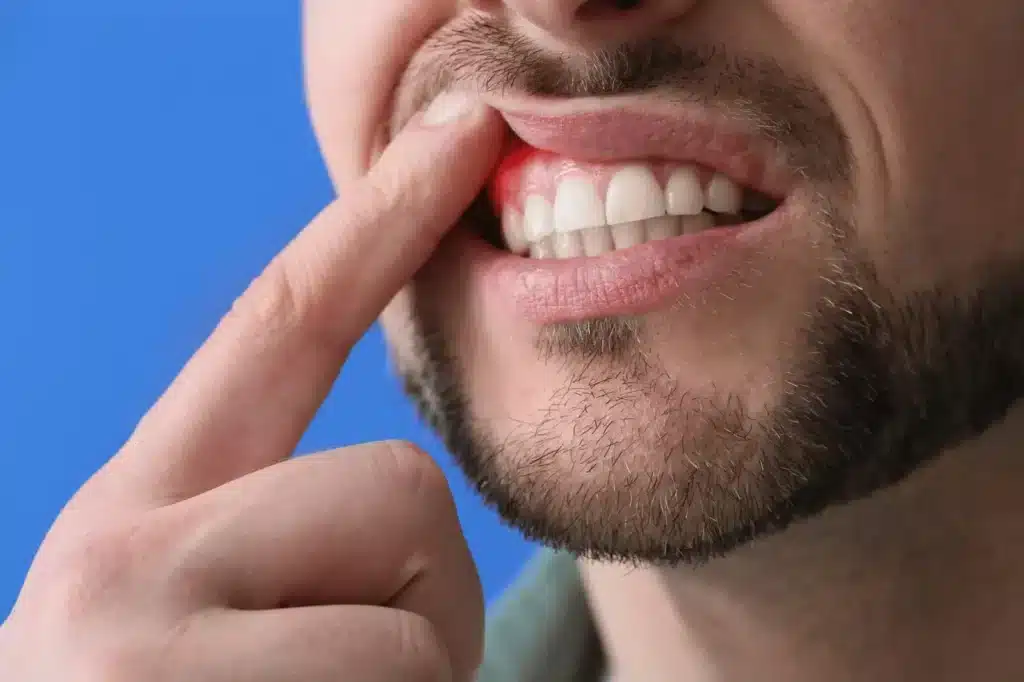
Oral health plays a significant role beyond just a beautiful smile. Gum disease and bone health are linked, directly influencing each other. The impact of tooth loss and gum disease on bone density is profound and can have far-reaching consequences for an individual’s health.
Gum Disease
Periodontitis, also known as gum disease, is an infection that affects the supporting structures of the teeth. One of its detrimental effects is causing bone loss, ultimately leading to tooth loss.
Causes of Gum Disease
The causes of gum disease include:
- Poor oral hygiene
- Plaque buildup
- Smoking or Tobacco use
- Pregnancy
- Hormonal Changes
- Genetics
- Diabetes or Immune System Disorders
- Age and Diet
Symptoms
Symptoms of gum disease may include:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing
- Receding gums or visible tooth roots
- Persistent bad breath (halitosis)
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Changes in the way teeth fit together when biting
- Pus between the teeth and gums
- Changes in the alignment of teeth or a change in the fit of dentures
- Sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures
- Pain or discomfort while chewing
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is characterized by a reduction in bone mineral density resulting from an imbalance between bone resorption and formation. As a consequence, the risk of bone fractures becomes elevated.
Relation between Gum Disease and Bone Health
The inflammation from gum disease can weaken bones and cause low bone mass, leading to tooth loss. Gum disease and bone health are linked and it does affect your health.
Poor oral hygiene results in swollen gums (gingivitis) and untreated, leads to periodontitis. Osteoporosis and gum disease can be mutual risk factors impacting bone loss. Gum disease destroys bone due to bacterial infestation, potentially contributing to osteoporosis development. Jaw bone resorption can lead to tooth loss and gum detachment.
Risk Factors for Bone Loss Due to Gum Disease
Shared risk factors for bone loss due to gum disease include:
- Old age
- Smoking
- Vitamin D deficiency
Gum disease may worsen bone loss if osteoporosis is already present.
Treatment
Curing gum disease and bone health involves a combination of professional dental treatments and good oral hygiene practices. Here are the steps to help cure gum disease:
- Professional Dental Cleanings
- Scaling and Root Planing
- Dental Implants for Missing Teeth
- Surgical Treatments
- Good Oral Hygiene
- Quit Smoking
- Antibiotics
- Tartar Control Treatments
Conclusion
Understand the crucial link between gum disease and bone health to avoid any serious health hazards. Prioritizing proactive measures for preserving bone health and enhancing overall well-being.


